
If this error message appears, cancel from adding the new file type. This file type, some Catalog items may not work properly.
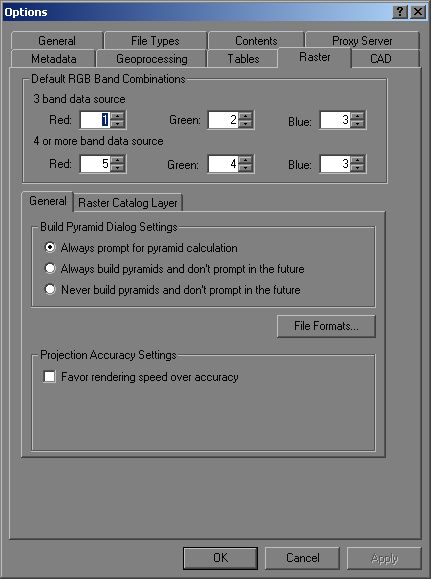
"" is a file type used by some Catalog items. Note:Īt 9.2 and 9.3, a warning message is returned if the file type is already in use in ArcGIS Desktop: That file type is once again displayed in ArcCatalog.įor a partial list of the recognized file types, refer to ArcCatalog > Customize > ArcCatalog Options, and the General and Raster tabs. If a new file type has been added to ArcCatalog > Customize > ArcCatalog Options > File Types tab, remove the file type, close ArcCatalog, and re-open it. Solution or Workaroundĭo not add any file type to this area in ArcCatalog, if a file with that extension already lists in the ArcCatalog Table of Contents. They do not list in ArcCatalog, cannot be selected for use in the tools in ArcToolbox, and are not available for drawing in ArcMap. DGN to this list renders files with these extensions invisible to ArcGIS. Projections cannot be defined, data cannot be re-projected, and in ArcMap, the projection of the Data Frame Properties cannot be changed.Ī second example is CAD data. PRJ to this area causes all projection files to disappear from ArcGIS. CauseĪdding a recognized file type to ArcCatalog > Customize > ArcCatalog Options > File Types tab creates a conflict within the software, and causes ArcGIS to 'forget' that the file type is already known.Īs an example, adding the file type. However, if you do copy a shapefile outside ArcGIS, be sure to copy all the files that make up the shapefile.Adding any file type that is already recognized by ArcGIS to this area causes that file type to disappear from ArcGIS. When copying shapefiles, it is recommended that you do so in ArcCatalog or by using a geoprocessing tool. The first tool is, which is the recommended tool as you can also simplify the map at the same time, reducing the file size.
Arcgis file extensions windows#
When viewing shapefiles in ArcCatalog (or any ArcGIS application), you will only see one file representing the shapefile however, you can use Windows Explorer to view all the files associated with a shapefile. cpg-An optional file that can be used to specify the codepage for identifying the characterset to be used.Įach file must have the same prefix, for example, roads.shp, roads.shx, and roads.dbf. xml-Metadata for ArcGIS-stores information about the shapefile. prj-The file that stores the coordinate system information used by ArcGIS.
Arcgis file extensions software#
The ESRI ArcGIS Desktop software is another program that can be used to view these TAB. tab format are created to store geological details of a particular location. mxs-Geocoding index for read/write shapefiles (ODB format). tab extension may consist of details that can be referenced when a user views an associated spatial data file using the MapInfo application. ixs-Geocoding index for read/write shapefiles. A new attribute indexing model has been developed for shapefiles and dBASE files.
ArcView GIS 3.x attribute indexes for shapefiles and dBASE files are not used by ArcGIS. Click the General tab and uncheck Hide file extensions. Choose Customize from the pull-down menu and click ArcCatalog Options. atx file is created for each shapefile or dBASE attribute index created in ArcCatalog. To configure ArcGIS for Desktop to show file extensions, uncheck the Hide file extensions check box in the ArcCatalog Options dialog box. aih-The files that store the attribute index of the active fields in a table or a theme's attribute table. fbx-The files that store the spatial index of the features for shapefiles that are read-only. sbx-The files that store the spatial index of the features. Attribute records in the dBASE file must be in the same order as records in the main file. There is a one-to-one relationship between geometry and attributes, which is based on record number. dbf-The dBASE table that stores the attribute information of features required.
shx-The index file that stores the index of the feature geometry required. shp-The main file that stores the feature geometry required. The shapefile format defines the geometry and attributes of geographically referenced features in three or more files with specific file extensions that should be stored in the same project workspace. A shapefile is one of the spatial data formats that you can work with and edit in ArcGIS. Data in ADF file can be exported to other image formats, such as BMP, TIFF, or JPG, by opening such file with ArcGIS and choosing appropriate option. Shapefiles are a simple, nontopological format for storing the geometric location and attribute information of geographic features. ADF is a filename extensions associated with a advanced geographic information platform ArcGIS developed by Esri.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
